今日推荐开源项目:《标准结局 jojogif》
今日推荐英文原文:《Functional vs Object-Oriented Programming》

今日推荐开源项目:《标准结局 jojogif》传送门:GitHub链接
推荐理由:将视频转换成一段 GIF 自然属于不算少见的功能,但是有的时候一些 GIF 可能需要一些特别的定制——比如令人熟悉的发黄的界面以及左下角的黄色箭头加上 TBC。这个项目可以为你用视频转换来的 GIF 自动加上标准结局,顺带一提标准结局的出处是动漫 JOJO 的奇妙冒险,一部每一个看过的人几乎都会向其他人推荐的传说之作。
今日推荐英文原文:《Functional vs Object-Oriented Programming》作者:Tomas Engquist
原文链接:https://medium.com/better-programming/functional-vs-object-oriented-programming-e5939c8105ff
推荐理由:面向对象和函数式编程二者的对比
Functional vs Object-Oriented Programming
Arguments over preferred languages (C++ vs Java, JavaScript vs Ruby, etc.) have always been prevalent in the programming community, however, programmers disagree on more than just language. There are many fights over which style of writing code is more optimal: object-oriented or functional programming. While OOP is by far the most popular programming design, many people have not even heard of functional programming. We’re going to explain the fundamental differences between object-oriented and functional programming and describe the advantages and disadvantages of each style.What Is Object-Oriented Programming?
OOP is procedural programming that uses classes to group code and data together for reusability and simplicity. By separating a program into classes, it is easier to modify parts of the program in isolation. Each class is a template for a type of object or an instance of the class. When placing methods into different classes, instances of each class can easily be modified, replaced, and reused. However, mutating class instances can get complicated with larger sets of data because it’s harder to track where each instance was changed.
By implementing methods inside a class, it is easy to mutate instances of the class. (JavaScript)
The advantages of OOP
Since its rise in popularity in the 1980s, object-oriented has been the principal design concept of software engineering. Java, C++, Python, and Ruby are the most commonly used OOP languages, but there are over 100 other programming languages that support OOP. These languages have been used to develop some of the most widely used programs in history. Gmail and Minecraft are written in Java, Instagram and Spotify are written in Python, Windows and OSX are written in C & C++. We will discuss four important concepts that make OOP a popular design strategy: intuitive problem solving, encapsulation, inheritance, and polymorphism.Intuitive problem solving
Programmers love OOP because it is easy to learn and conceptualize. OOP places classes in a hierarchy of parents and their children. Humans organize things in a similar hierarchical manner. For example, a vehicle is something that moves things. A car is a vehicle travels over roads. A hybrid is a car that uses electricity in addition to gas. A Prius is a hybrid with five seats made by Toyota. Note that in each sentence, we use the previously defined object to help conceptualize the new, more specific object. In short, OOP makes sense to us.Inheritance
Probably the biggest advantage of using OOP is inheritance, or reusing code. Going back to the Prius example, let’s imagine you are a car manufacturer. If you want to switch from producing Priuses to the Honda Insight, you don’t have to research how to make a vehicle, car, or hybrid. Why? Instead of starting from scratch, you can take your blueprint for making and work from there. In OOP, the class is the equivalent of the blueprint. Instead of starting every program from scratch, you can inherit a class that contains any methods or properties that you need (or a hybrid) and then add new features on top of it (Prius, Insight). Inheriting classes keeps your code DRY (don’t repeat yourself) and saves you lots of time.
The Hybrid class inherits all the Car class methods while keeping access to its own class methods. (JavaScript)
Encapsulation
OOP allows us to create objects of a certain class. Many OOP programming languages have a way to protect variables from outside access, forcing programmers to only interact with the class through specific methods. This allows us to hide our implementation behind an interface (protecting objects from programmer mistakes) and interact with other parts of the program through these well-behaved interfaces. In addition to providing this security, encapsulation also helps us make flexible code that is easy to change and maintain.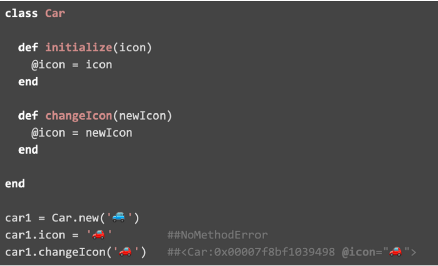
Encapsulation prevents the object attributes from being directly modified. (Ruby)
Polymorphism
The literal definition of polymorphism is the condition of occurring in several different forms. In OOP, polymorphism refers to the ability of a variable, function or object to take on multiple forms and have multiple behaviors. This allows us to reuse code in a similar way to inheritance. Going back to our previous example, let’s say we have a vehicle class with a method move. All the subclasses of vehicle can reuse this method move but with different behavior. The car subclass will start spinning its wheels, the boat subclass will start spinning its propellers, and the plane subclass will start spinning its turbines. This cuts down the work of the developers because they can now create a general class with certain behaviors and make small altercations to subclasses when they need something more specific.
Polymorphism allows us to reuse move() with different functionality (C++)
In dynamic languages we use for the web, this behavior is kind of built-in. Functions that accept “vehicle-like” objects already behave polymorphically, spinning the car’s wheels, and the boat’s propellers. In other languages, polymorphism is just as important but needs to be implemented explicitly.
Without OOP, implementing this kind of polymorphism can get very ugly. “Simple” way of simulating it usually involves keeping track of type and writing if statements everywhere polymorphism is desired. Other common methods of implementing polymorphism without OOP get progressively more complex as the “level” of polymorphism increases.
The disadvantages of OOP
While OOP reigns king as the most popular program design, developers have certainly encountered issues with it. In many cases, the advantages of OOP come with side effects and additional burdens. In this section, we will go through some of these burdens and how they can affect programs.Monkey Banana Problem
Inheritance is one of the most important concepts in OOP. It allows for the reuse of code by basing Objects or Classes on other Objects and implementing methods defined in the parent classes. Reuse of code through inheritance cuts down on redundant code and makes OOP programming seem like a no brainer, that should be a part of every programming language. But just like everything in life, there are tradeoffs that come with inheritance. The main problem has been famously stated by Joe Armstrong, the creator of the ERLANG language.“ You wanted a banana but what you got was a gorilla holding the banana and the entire jungle.”Classes in OOP may be deeply nested, which means they have a long chain of parents classes they rely on. When inheriting a deeply nested class, you must also inherit its parent class and that parent’s parent class and that parent’s parent’s parent class and so forth. Programs won’t compile until you inherit all of the necessary parent classes. A solution to this is to avoid writing deeply nested classes, but that takes away from the reusability that comes with inheritance.
Encapsulation Problem
Inheritance creates several dependencies between parent and child classes. It becomes difficult to understand what is happening in the child class without having to open the parent class. Furthermore, the child class has access to the parent class methods and might overwrite these methods. Encapsulation is done to prevent Object variables from being tempered by child classes. The parent class constructor in Javascript makes a deep copy of the Object and then passes it by reference. Making copies of each parent class bogs down on the efficiency of the program.What is Functional Programming?
Functional programming is similar to “pure” mathematical functions. Instead of specifying a procedure to solve a problem, functional programs compose functions to produce the desired result without using ‘state’. Evaluation of these functions and their relationships are much more important than objects and relationships. Functional programming also makes very little use of variables. Variables depend on state, which changes based on the past path of a program. Once state is involved, the function can’t be evaluated in isolation — making it no longer pure.The advantages of functional programming
Surprisingly, functional programming also has many of the same perks as OOP. Many of these advantages come without the burdens that come with OOP.Eliminate race conditioning
A race condition exists when two different functionalities depend on a common resource. When the sequence of events occurs differently than expected by the programmer, a failure occurs. This may occur when fetching data from an API. For example, let’s say you have a method displayData(data) that uses data from an API and another method to retrieveData() that fetches it. If you run displayData(retrieveData()), the fetch may not finish in time and displayData will try to run before retrieveData is finished, resulting in an error. Functional programs do not share resources and create dependencies in this manner, avoiding race conditioning altogether.Polymorphism
Wait, wasn’t polymorphism supposed to be an advantage for OOP? Yes, it still is, but the truth is you don’t need to use OOP to implement polymorphism. Interfaces will give you this without all of the monkeys, bananas, and jungles of OOP.Easy debugging
Functions in functional programming are ‘pure’ i.e. you expect the same output given the same input. The functional approach stresses simple functions that provide one piece of functionality. Bigger tasks are modularized into multiple simpler functions. In theory, the lack of state makes it much easier to debug these programs.Reusability
In the words of Joe Armstrong:“If you have referentially transparent code, if you have pure functions — all the data comes in its input arguments and everything goes out and leave no state behind — it’s incredibly reusable.”Because every function is pure, one can keep reusing them without ever having to worry about state. In OOP, the state of class may change, whether intentional or not and affect the results of the instance or class methods.
Disadvantages of functional programming
You can’t really break down the disadvantages of functional programming into different categories. The one main problem with functional programming is quite straightforward: it’s very hard. Because we don’t have the structure and organization that comes with OOP, writing and reading complex functional programs is quite difficult. When lovers of functional programming claim that it is easier to debug and is more reusable than OOP, you must take it with a grain of salt. While it is true that pure functions don’t rely on state, they still can get complicated, difficult to follow, and hard to debug.Conclusion
Clearly, it’s not so easy to pick a side between OOP and functional programming. The good thing is, you don’t have to. The only thing you have to determine is where to use each approach. Some programs might be better off written with object-oriented design while others might be better off written with functional design. Some programs might be better off using a combination of both. As a programmer, it is your job to make these choices. Hopefully, you can now make these informed choices.下载开源日报APP:https://opensourcedaily.org/2579/
加入我们:https://opensourcedaily.org/about/join/
关注我们:https://opensourcedaily.org/about/love/